Stacked Lithium Batteries are at the forefront of a transformation in energy storage solutions, offering unprecedented efficiency and versatility. As energy demands continue to escalate globally, innovative technologies like the Stacked Lithium Battery provide a promising alternative to traditional energy storage systems. Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in battery technology, emphasizes the significance of this advancement by stating, "Stacked Lithium Batteries represent a shift towards more compact and efficient energy storage, essential for both consumer applications and large-scale energy management."
The unique design of Stacked Lithium Batteries allows for higher energy density and improved thermal management, making them ideal for a range of uses from electric vehicles to renewable energy sources. With sustainability becoming a critical focus, these batteries not only enhance performance but also contribute to the reduction of environmental impacts associated with conventional energy systems. As industries look for innovative storage solutions, the integration of Stacked Lithium Batterie technology stands out as a crucial step toward a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.

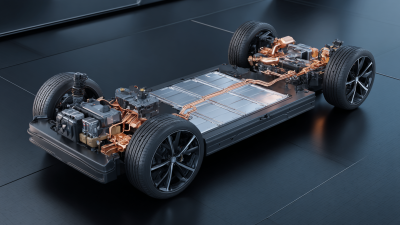
Stacked lithium battery technology is at the forefront of innovation in energy storage solutions, representing a significant advancement in how we harness and utilize electrical energy. At the core of this technology are individual lithium cells that are carefully stacked to optimize space and increase energy density. Each cell consists of a cathode, an anode, and an electrolyte, all of which play crucial roles in the battery's performance. The cathode, typically made from lithium compounds, serves as the source of lithium ions during discharge, while the anode, often composed of graphite, allows for lithium ion intercalation during charging. The electrolyte, which is a lithium salt dissolved in a solvent, facilitates the movement of ions between the cathode and anode, enabling efficient energy transfer.
Moreover, the structural design of stacked lithium batteries enhances their thermal management and safety attributes. By stacking cells vertically or horizontally, manufacturers can minimize the overall footprint while maximizing energy output. This design also aids in heat dissipation, critical for maintaining battery longevity and performance. The integration of advanced materials, such as solid-state electrolytes, can potentially eliminate risks associated with liquid electrolytes, such as leakage or combustion, leading to safer and more reliable energy storage systems. As demand for efficient energy solutions grows, stacked lithium battery technology will undoubtedly continue to evolve, offering improved performance for various applications from electric vehicles to renewable energy systems.
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Amount of energy stored per unit volume | 250 Wh/L |
| Cycle Life | Number of cycles before capacity drops below 80% | 3000 cycles |
| Charging Time | Time taken to fully charge the battery | 1-2 hours |
| Operating Temperature | Range of temperatures for safe operation | -20°C to 60°C |
| Self-Discharge Rate | Rate at which battery loses charge when not in use | 5% per month |
| Voltage Range | Battery voltage during operation | 3.2 - 4.2 V |

Stacked lithium batteries are ushering in a new era for energy storage solutions, significantly outperforming traditional options. One of the most compelling advantages of stacked lithium batteries is their high energy density, which allows for more power to be stored in a compact form. According to a recent industry report by the International Energy Agency, stacked lithium batteries can achieve energy densities of up to 250 Wh/kg, compared to traditional lead-acid batteries that typically offer around 30-50 Wh/kg. This efficiency not only improves space utilization but also enhances the overall performance of energy systems.
Moreover, the lifespan of stacked lithium batteries surpasses that of traditional batteries. Studies indicate that lithium batteries can last anywhere from 2,000 to 7,000 charge cycles, depending on usage, which is significantly longer than the 500-1,000 cycles of conventional lead-acid batteries. This durability translates into reduced costs over time, as users experience fewer replacements and lower maintenance needs. This longevity positions stacked lithium technology as a more sustainable choice for consumers looking to minimize their environmental impact.
Tips: When considering an energy storage solution, evaluate your energy needs and usage patterns. A stacked lithium battery may require a larger upfront investment, but the long-term savings and efficiency can make it a worthwhile choice. Additionally, ensure proper management systems are employed to maximize battery lifespan and performance in your specific application.

The advent of stacked lithium batteries has brought transformative advancements across various industries. One of the most significant applications is in renewable energy, where these batteries enable efficient storage solutions for solar and wind energy. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, battery storage capacity is projected to reach up to 2000 GWh by 2040, significantly enhancing the reliability and stability of energy supply from intermittent renewable sources. Stacked lithium batteries, with their higher energy density and longer lifecycle, play a crucial role in enabling this shift towards sustainable energy.
In the electric vehicle (EV) sector, stacked lithium batteries are paving the way for longer driving ranges and faster charging times. Research indicates that EVs are expected to dominate the global automotive market by 2030, with sales forecasted to exceed 30 million units per year. The scalability of stacked battery technology allows for lighter and more compact designs, which directly contribute to the performance and efficiency improvements sought by manufacturers and consumers alike. Moreover, their application in smart grid technologies further exemplifies their versatility; they facilitate real-time energy management, reduce energy costs, and enhance grid reliability, thus redefining energy consumption paradigms.
The rise of stacked lithium batteries marks a significant advancement in the field of energy storage, yet it is not without challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is the thermal management of these systems. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the risk of thermal runaway increases in densely packed battery configurations, necessitating advanced cooling strategies. Failure to manage these temperatures can lead to safety hazards, which are a substantial barrier to widespread adoption in critical applications such as electric vehicles and large-scale energy systems.
Moreover, the manufacturing complexity associated with stacked lithium battery systems presents another significant challenge. While the energy density of stacked configurations is notably higher, this added complexity also elevates production costs and time. The Market Research Future report estimates that the levelized cost of energy from battery storage systems can be up to 30% higher due to these manufacturing intricacies. Furthermore, recycling and end-of-life management remain pressing concerns as the industry grows; efficient processes are still in development to handle the significant waste generated by these advanced battery systems. Thus, as the technology continues to evolve, addressing these challenges will be crucial for harnessing the full potential of stacked lithium batteries in energy storage solutions.
The future of energy storage is being reshaped by innovations in stacked lithium battery technology. One of the most significant trends is the push towards higher energy density and efficiency. Researchers are focusing on enhancing the electrochemical performance of stacked batteries by utilizing advanced materials and electrode designs. Innovations such as solid-state batteries promise not only to improve safety but also to increase energy storage capacity, making these batteries suitable for a wider range of applications including electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
Another area of development is the integration of smart technology in stacked lithium batteries. Intelligent battery management systems are being designed to monitor and optimize performance in real-time. These systems can enhance operational longevity and ensure that the batteries operate within safe parameters. Furthermore, the incorporation of AI and machine learning algorithms is enabling predictive maintenance, which can significantly reduce downtime and improve reliability.
As these technologies advance, we can expect stacked lithium batteries to play a crucial role in the transition towards more sustainable energy solutions, playing an essential part in mitigating the challenges of climate change and energy sustainability.