
The shift towards renewable energy has accelerated in recent years. According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global off-grid solar market is expected to reach 3 billion people by 2030. This growing trend highlights the importance of effective energy solutions. An Off Grid Hybrid Inverter plays a pivotal role in harnessing this potential.
When selecting an Off Grid Hybrid Inverter, understanding your unique needs is essential. Many users overlook crucial details, such as power output and battery compatibility. It is easy to get lost in features that sound impressive, yet may not serve actual energy requirements. Reports indicate that poor inverter choices can lead to inefficiencies, costing users more in the long run.
In the realm of sustainable energy, not all hybrid inverters are created equal. The market offers a wide range of products, and the wrong choice could mean inadequate power supply. Evaluating options with a critical eye is vital. Too often, buyers neglect to consider long-term performance and support. This can lead to regret and unnecessary expenses later. By taking the time to choose wisely, users can set themselves up for success in their off-grid journey.
When choosing an off-grid hybrid inverter, understanding its key features is crucial. These inverters are versatile, allowing for the use of solar energy and battery storage. They can either be used independently or connected to the grid. Look for models with high efficiency ratings. A reliable inverter should convert energy effectively, minimizing losses. Pay attention to the inverter's maximum input power. This determines how much energy your system can handle.
Another important element is the number of AC outputs. More outputs mean more appliances can run simultaneously. Examine the inverter’s compatibility with various battery types. Not all inverters work with every battery technology. Some may require specific settings or additional components. Keep in mind that the size and weight of the unit matter, especially for limited spaces.
Consider ease of use and installation as well. Some models come with complex instructions. This can be frustrating and time-consuming. A user-friendly interface is always a plus. Lastly, think about warranty and support. Some products may promise the world but lack reliable backup. Choosing an inverter is not a simple task. Reflect on your energy needs and future expansion plans.
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Power Rating | The maximum power output the inverter can deliver. | Critical for determining load capacity. |
| Efficiency | The ratio of output power to input power, usually expressed as a percentage. | Higher efficiency means less energy loss. |
| Battery Compatibility | Compatibility with different types of batteries (lead-acid, lithium-ion, etc.). | Ensures optimal performance and longevity. |
| Transfer Time | The time it takes for the inverter to switch from grid to battery power. | Shorter transfer times enhance system reliability. |
| Inverter Type | Pure sine wave vs modified sine wave inverters. | Pure sine wave is necessary for sensitive electronics. |
| User Interface | The ease of use of the inverter's display and controls. | A user-friendly interface simplifies system management. |
| Cooling System | Type of cooling method (air-cooled or liquid-cooled). | Effective cooling prolongs inverter lifespan. |
| Warranty and Support | Length of warranty and availability of customer support. | A good warranty and support increase peace of mind. |
| Dimensions and Weight | Physical size and weight which may affect installation. | Consider space and mounting options in your setup. |
| Cost | The overall price of the inverter. | Budget constraints will dictate choice and features. |
When choosing an off-grid hybrid inverter, it's crucial to understand your power needs. The average household consumes around 877 kWh per month, but this varies widely. Assessing your energy consumption helps you select the right inverter capacity. Start by listing all your appliances—refrigerators, lights, and electronics. Don’t forget the peak power demand during usage.
Tip 1: Use an energy monitor. This device can track your usage in real-time. Monitoring your consumption can reveal surprising insights. You might find some devices consume more energy than expected. This knowledge allows you to make informed choices.
Tip 2: Plan for future needs. Households often grow, adding items like electric vehicles or more appliances. Anticipating those changes aids in selecting an inverter that won’t become obsolete.
Conducting a detailed energy assessment is vital. Some reports show that up to 30% of households overestimate their power needs. This miscalculation can lead to purchasing an overly large inverter, wasting resources. Make adjustments based on actual usage data for better efficiency. Set realistic goals and adjust accordingly.
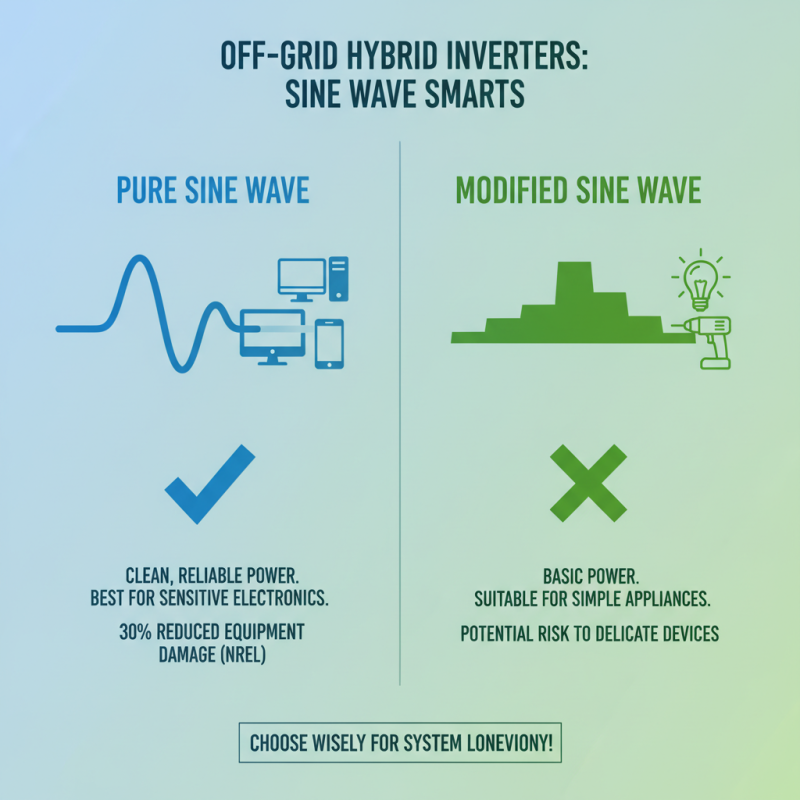
When selecting an off-grid hybrid inverter, understanding the differences between pure sine wave and modified sine wave is crucial. Pure sine wave inverters provide power that closely resembles traditional utility power. This smooth waveform supports sensitive electronics. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, using a pure sine wave inverter reduces the risk of equipment damage by 30%.
On the other hand, modified sine wave inverters are more affordable but may not work well with all devices. They generate a stair-step waveform that can interfere with sensitive electronics. The U.S. Department of Energy reports that these inverters can cause overheating in appliances, reducing their lifespan by up to 50%. It's important to consider your specific needs before making a choice.
In many cases, the initial savings of a modified sine wave inverter come with hidden costs. An incorrectly powered device may lead to extra expenses in repairs or replacements. When evaluating your options, consider how often you'll use sensitive equipment. For some, the lower initial cost may not be worth the potential long-term damage.
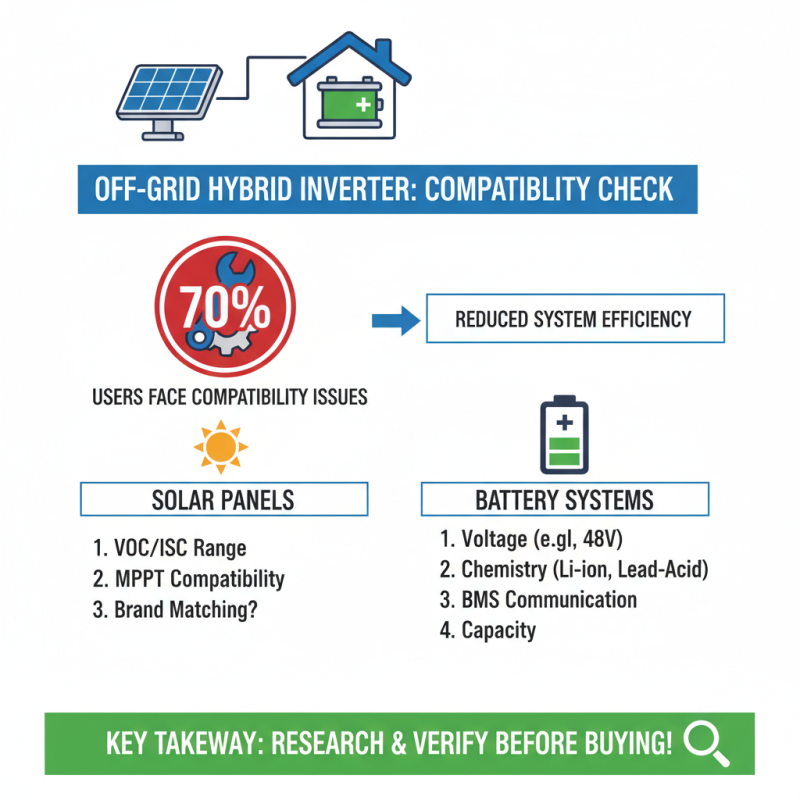
When selecting an off-grid hybrid inverter, compatibility with solar panels and battery systems is crucial. According to a recent industry report, 70% of users encounter compatibility issues that reduce system efficiency. This highlights the need for thorough research before making a purchase.
One tip is to check the inverter’s input voltage range. Most solar panels operate between 30-60 volts. Ensuring your inverter accommodates this range is essential for optimal energy extraction. Another consideration is the inverter's ability to handle the battery type. Li-ion batteries require specific charging profiles that not all inverters support.
Additionally, consider the inverter's power rating. A mismatch between the inverter and your solar array can lead to energy wastage. For example, if your inverter can handle 3,000 watts and your panels generate 4,000 watts, you’ll lose potential energy. Regularly assess your energy needs to avoid oversizing or undersizing your inverter. This reflection on actual usage patterns can help enhance long-term efficiency.
When analyzing cost versus performance for your off-grid hybrid inverter, budgeting is crucial. You need to balance performance features and initial costs. High-capacity inverters often come at a premium, but they deliver efficiency and reliability. Cheaper models may save you money upfront but can lead to higher energy loss and maintenance costs later.
Consider your energy needs carefully. Assess how much power you will consume daily. This will help you determine the right inverter size. Also, think about future needs. If you plan to expand your energy system, reserve some budget for a larger inverter.
Don’t forget about installation costs. Sometimes, they can be more than the inverter itself. Hiring a professional may increase expenses, but it guarantees safety. If you choose DIY, make sure you’re well-informed. Mistakes can lead to costly repairs. Balancing all these elements can be challenging, but it is essential for long-term satisfaction.





